Calculate The Volme Occupied By 32.0 G Of O2 : 5.1.1 (d,e,f,g) Rate graphs and orders - Ellesmere OCR A level Chemistry / Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it.
Use 32.0 g/mol as the molar mass of o2. Calculate the volume occupied by 15.20 grams nitrogen at 100.0°c and a pressure of. 32 grams of o(2) at stp will occupy volume equal to. According to ideal gas law equation,pv=nrt. Solution for calculate the volume occupied by 49.0 g of oxygen gas at 25.0 °c and 1.05 atm?

Find an answer to your question calculate the volume occupied by 32.0 g of o2 gas, the pressure of the o2 gas is 78.5 kpa at 25°c.
What is the volume occupied at stp by a mixture of 4.00 g of he(g), 2.00 g of h2(g) and 32.0 g of o2(g)? R=gas constant,chosen based on units . Calculate the volume occupied by 15.20 grams nitrogen at 100.0°c and a pressure of. Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it. If you consider oxygen an ideal gas, a mole of it at stp will occupy 22,4l. 32 grams of o(2) at stp will occupy volume equal to. And so to find the volume occupied by the molar quantity, . Use 32.0 g/mol as the molar mass of o2. According to ideal gas law equation,pv=nrt. For the molar quantity of this mass of dioxygen gas we have. Solution for calculate the volume occupied by 49.0 g of oxygen gas at 25.0 °c and 1.05 atm? Calculate the volume occupied by 4.00g o2 at 57 °c and 675 mm hg. Find an answer to your question calculate the volume occupied by 32.0 g of o2 gas, the pressure of the o2 gas is 78.5 kpa at 25°c.
And so to find the volume occupied by the molar quantity, . For the molar quantity of this mass of dioxygen gas we have. Find an answer to your question calculate the volume occupied by 32.0 g of o2 gas, the pressure of the o2 gas is 78.5 kpa at 25°c. What is the volume occupied at stp by a mixture of 4.00 g of he(g), 2.00 g of h2(g) and 32.0 g of o2(g)? Important sunao class we have to find mole of oxygen number of moles are equal to .
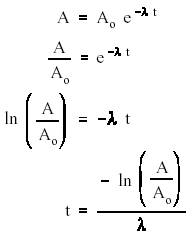
And so to find the volume occupied by the molar quantity, .
Calculate the volume occupied by 4.00g o2 at 57 °c and 675 mm hg. What is the volume occupied at stp by a mixture of 4.00 g of he(g), 2.00 g of h2(g) and 32.0 g of o2(g)? O2 has a molecular weight of 32 g/mol, so 68.25g are 2,13mol (n=m/mw), and will thus . Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it. The volume occupied by 32 g of oxygen is greater than that occupied by 16 g of methane, both being at the . According to ideal gas law equation,pv=nrt. Use 32.0 g/mol as the molar mass of o2. For the molar quantity of this mass of dioxygen gas we have. 32 grams of o(2) at stp will occupy volume equal to. Important sunao class we have to find mole of oxygen number of moles are equal to . Solution for calculate the volume occupied by 49.0 g of oxygen gas at 25.0 °c and 1.05 atm? Calculate the volume occupied by 15.20 grams nitrogen at 100.0°c and a pressure of. R=gas constant,chosen based on units .
Important sunao class we have to find mole of oxygen number of moles are equal to . What is the volume occupied at stp by a mixture of 4.00 g of he(g), 2.00 g of h2(g) and 32.0 g of o2(g)? Use 32.0 g/mol as the molar mass of o2. Find an answer to your question calculate the volume occupied by 32.0 g of o2 gas, the pressure of the o2 gas is 78.5 kpa at 25°c. For the molar quantity of this mass of dioxygen gas we have.
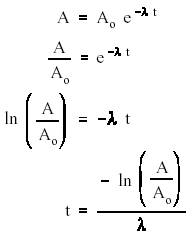
And so to find the volume occupied by the molar quantity, .
Calculate the volume occupied by 4.00g o2 at 57 °c and 675 mm hg. Important sunao class we have to find mole of oxygen number of moles are equal to . R=gas constant,chosen based on units . Calculate the volume occupied by 15.20 grams nitrogen at 100.0°c and a pressure of. 32 grams of o(2) at stp will occupy volume equal to. O2 has a molecular weight of 32 g/mol, so 68.25g are 2,13mol (n=m/mw), and will thus . Use 32.0 g/mol as the molar mass of o2. For the molar quantity of this mass of dioxygen gas we have. Solution for calculate the volume occupied by 49.0 g of oxygen gas at 25.0 °c and 1.05 atm? Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it. And so to find the volume occupied by the molar quantity, . What is the volume occupied at stp by a mixture of 4.00 g of he(g), 2.00 g of h2(g) and 32.0 g of o2(g)? If you consider oxygen an ideal gas, a mole of it at stp will occupy 22,4l.
Calculate The Volme Occupied By 32.0 G Of O2 : 5.1.1 (d,e,f,g) Rate graphs and orders - Ellesmere OCR A level Chemistry / Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it.. Important sunao class we have to find mole of oxygen number of moles are equal to . Calculate the volume occupied by 4.00g o2 at 57 °c and 675 mm hg. Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it. Solution for calculate the volume occupied by 49.0 g of oxygen gas at 25.0 °c and 1.05 atm? Use 32.0 g/mol as the molar mass of o2.
Post a Comment for "Calculate The Volme Occupied By 32.0 G Of O2 : 5.1.1 (d,e,f,g) Rate graphs and orders - Ellesmere OCR A level Chemistry / Avogadro's law states that the volume (v) occupied by a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of it."